Xaoc Jena Handleiding
Xaoc
Niet gecategoriseerd
Jena
Bekijk gratis de handleiding van Xaoc Jena (8 pagina’s), behorend tot de categorie Niet gecategoriseerd. Deze gids werd als nuttig beoordeeld door 5 mensen en kreeg gemiddeld 5.0 sterren uit 3 reviews. Heb je een vraag over Xaoc Jena of wil je andere gebruikers van dit product iets vragen? Stel een vraag
Pagina 1/8

binary
transfunc-
tioner
Model of 1989
operator’s manual rev. 1989/X1/1.2
JENA
THE LEIBNIZ BINARY SUBSYSTEM
SALUT
Thank you for purchasing this Xaoc Devices
product. Jena is a digital module that
and audio signals, a wavetable oscillator, a
Walsh function generator, or a rhythm genera-
tor. Jena is a new member of the Leibniz Binary
Subsystem which operates on signals and volt-
ages by manipulating binary 8-bit numbers.
The Leibniz subsystem offers direct access to
all individual bits of data which can be mixed
and cross-patched (like in the popular circuit
bending experimental technique, but without
the risk of damaging your device). Please note
that for analog inputs and outputs it needs to
be paired with other Leibniz modules, such as
Drezno. Complex chains will be possible as more
components are added to the system. For ex-
ample, you can use two Lipsk expanders (one
before Jena, and another one after Jena in the
chain) for unlimited patching.
INSTALLATION
The module requires 8hp worth of free space
in the eurorack cabinet. Always turn the pow-
er off before plugging the module into the bus
board using the supplied ribbon cable. Pay
close attention to power cable pinout and ori-
entation. The red stripe indicates the negative
rail and should match the dot or –12V mark on
the bus board as well as the unit. Jena is inter-
nally secured against reversed power connec-
tion, however rotating the 16-pin header may
cause serious damage to other components
of your system, because it will short circuit the
+12V and +5V power lines. Always pay partic-
ularly close attention to the proper orientation
of your ribbon cable on both sides! Besides the
power cable, you will also need to connect Jena
to other components of your Leibniz Subsys-
tem. For this purpose, Jena comes equipped
with a single 10/10-pin ribbon cable, and
there should also be at least one such cable
included with your other Leibniz module(s).
The general logic is simple: connect inputs to
outputs. For example, you can use one ribbon
to join the out header of your Drezno to the
in header of Jena, and another to connect the
out in header of Jena to the header in Drezno.
This will make the data from the ADC section
in Drezno pass through Jena before returning
to the DAC section in Drezno.
It is a good idea to have all your Leibniz mod-
ules connected before mounting them in the
2
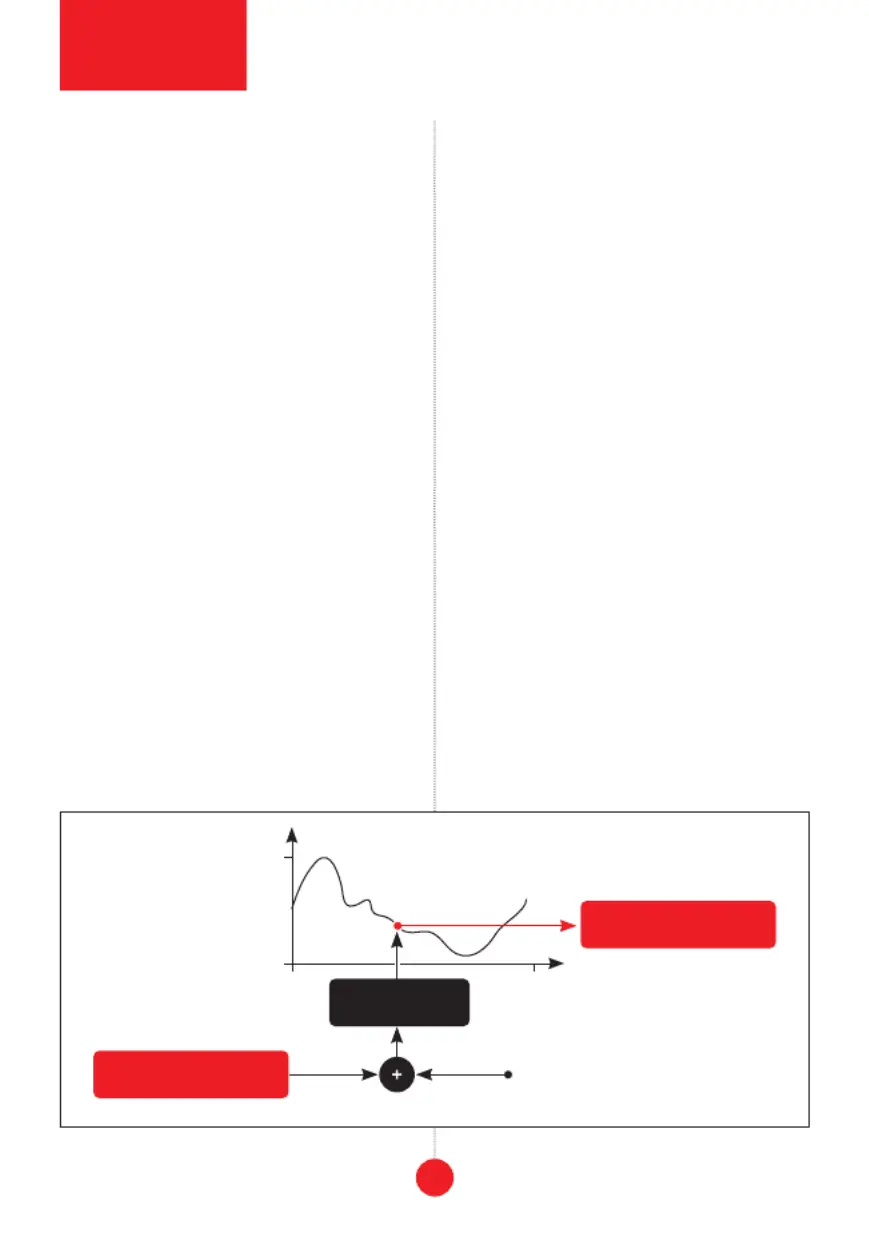
module
explained
2550
0
255
leibniz data bus
leibniz data bus
modulo 256
Phase CV
Output
Input
data processing principle of jena
case. Again, pay attention to the markings on
the boards and always connect the ribbon ca-
ble so that the red stripe matches the dot mark
on the board. For technical reasons, these dot
marks may not always face down. be care-
ful, as wrong connections may damage
the delicate digital circuits! All units
should be fastened by mounting the supplied
screws before powering up.
MODULE OVERVIEW
The main purpose of Jena is to map incoming
digital data to some other digital data through
a transfer function selected from its waveform
shape bank. For example, Jena may be con-
nected in a loopback to a Drezno module so
as to transform input analog waveforms to
some other output analog waveforms via the
ADC and DAC sections in Drezno. Jena allows
one to waveshape signals through the classic
table look-up technique: input 8-bit values are
treated as arguments of a function stored in
memory and values read from successive loca-
1). You can also feed a simple sawtooth or a tri-
angle wave from your VCO and it will be trans-
formed into variety of waveshapes (from 11
wavetable banks) with the additional option
of through-zero (DX-style) phase modulation.
The shape of the wave may be also morphed
with the panel knob and/or external CV.
Individual bit outputs on Jena may also be
used to produce interesting signals. There is a
dedicated bank of Walsh functions that can be
used for an unusual twist on additive synthe-
sis. Also, transforming slow waveforms to se-
quences of binary signals using the individual
bit outputs is a great way to create rhythmic
drum patterns. Jena comes with a special bank
of 256 modern drum loops split to individual
voice triggers.
controls as well as a 1+3 digit LED display.
During normal operation, the display shows
the currently selected bank of shapes or func-
tions
1
as well as the current shape number
within the bank
2
. Additional information
is displayed during operating mode selection.
The endless rotary encoder below the display
3
allows for manual selection of the current
bank or shape. A short press on the encoder
switches between the bank and shape layer. A
small dot on the display indicates which layer
is currently selected for editing. Both the bank
number and shape/function number may be
additionally controlled via the corresponding
bank
4
and shape
5
CV inputs that accept
-5V to +10V. The voltage values add to the panel
selection. The second knob, phase
6
, sets the
initial phase of the waveform which can also be
modulated by external CV via the phase jack
7
. The range of modulation is -5V to 5V which
corresponds to the phase change of four full cy-
cles. The blue link button
8
controls whether
the processed input data in Jena is passed to its
Leibniz output (the ribbon cable connected at
the back). When unlinked, the incoming data
is passed through unaffected. Regardless of the
status of the link button, the processed data is
always available from eight bit outputs jacks
9
in the form of eight binary gate (5V) signals
corresponding to individual bits (as with the
other Leibniz modules). The cluster of yellow
LEDs
10
indicates the bit outputs' activity.
The central red LED
11
indicates whether Jena
is operating in the asynchronous (waveshaper)
or synchronous (oscillator) regime.
CLOCKING AND SYNCHRONOUS/
ASYNCHRONOUS OPERATION
The incoming data is delivered to Jena through
the Leibniz interface which transmits all bits
alongside the data clock. For example, if you
connect Jena to Drezno, samples will be trans-
3
Product specificaties
| Merk: | Xaoc |
| Categorie: | Niet gecategoriseerd |
| Model: | Jena |
Heb je hulp nodig?
Als je hulp nodig hebt met Xaoc Jena stel dan hieronder een vraag en andere gebruikers zullen je antwoorden
Handleiding Niet gecategoriseerd Xaoc

5 Augustus 2025

5 Augustus 2025

5 Augustus 2025

5 Augustus 2025

5 Augustus 2025

5 Augustus 2025

5 Augustus 2025

5 Augustus 2025

5 Augustus 2025

4 Augustus 2025
Handleiding Niet gecategoriseerd
- Flir
- Vox
- Marquant
- Ruger
- Doomoo
- Solac
- Emko
- Musicmate
- Budda
- Steiner
- GeoVision
- Bauknecht
- Elac
- Ansmann
- IBox
Nieuwste handleidingen voor Niet gecategoriseerd

6 Augustus 2025

6 Augustus 2025

6 Augustus 2025

6 Augustus 2025

6 Augustus 2025

6 Augustus 2025

6 Augustus 2025

6 Augustus 2025

6 Augustus 2025

6 Augustus 2025