Microchip MCP3301 Handleiding
Microchip Niet gecategoriseerd MCP3301
Bekijk gratis de handleiding van Microchip MCP3301 (6 pagina’s), behorend tot de categorie Niet gecategoriseerd. Deze gids werd als nuttig beoordeeld door 93 mensen en kreeg gemiddeld 4.2 sterren uit 9 reviews. Heb je een vraag over Microchip MCP3301 of wil je andere gebruikers van dit product iets vragen? Stel een vraag
Pagina 1/6
2002 Microchip Technology Inc.DS00842A-page 1
MAN842
INTRODUCTION
True differential converters can offer many advantages
over single-ended input A/D Converters (ADC). In addi-
tion to their common mode rejection ability, these con-
verters can also be used to overcome many DC biasing
limitations of common signal conditioning circuits.
Listed below are some typical application issues that
can be solved with proper biasing of a differential con-
verter:
•Limited output swing of amplifiers
•Unwanted DC-bias point
•Low level noise riding on ground
•Unwanted or changing common mode level of
input signal
This application note discusses differential input config-
urations and their operation, circuits to implement
these input modes and techniques in choosing the cor-
rect voltage levels to overcome the previously
mentioned challenges.
DIFFERENTIAL AND SINGLE-ENDED
INPUT CONFIGURATIONS
Before discussing biasing solutions, it is important to
understand the functionality of differential A/D convert-
ers. The true differential A/D converter outputs a digital
representation of a differential input signal, typically a
two’s complement binary formatted output. The con-
verter output can be either signed positive or negative,
depending on the voltage level of the differential pair.
The following equation expresses this relationship for
the MCP330X devices:
EQUATION:
The binary output for the MCP330X is a 13-bit output
(12-bit plus sign output).
It is important to note that the converter output is zero
when the inputs are equal. As the voltage difference
between IN+ and IN- increases, the output code also
increases. The maximum voltage at which digital code
saturation will occur is VREF. The differential conver-
sion of the MCP330X converters will reject any DC
common mode signal at the inputs. For the MCP330X
converters, the common mode input range is rail-to-
rail, VSS-0.3V to VDD+0.3V.
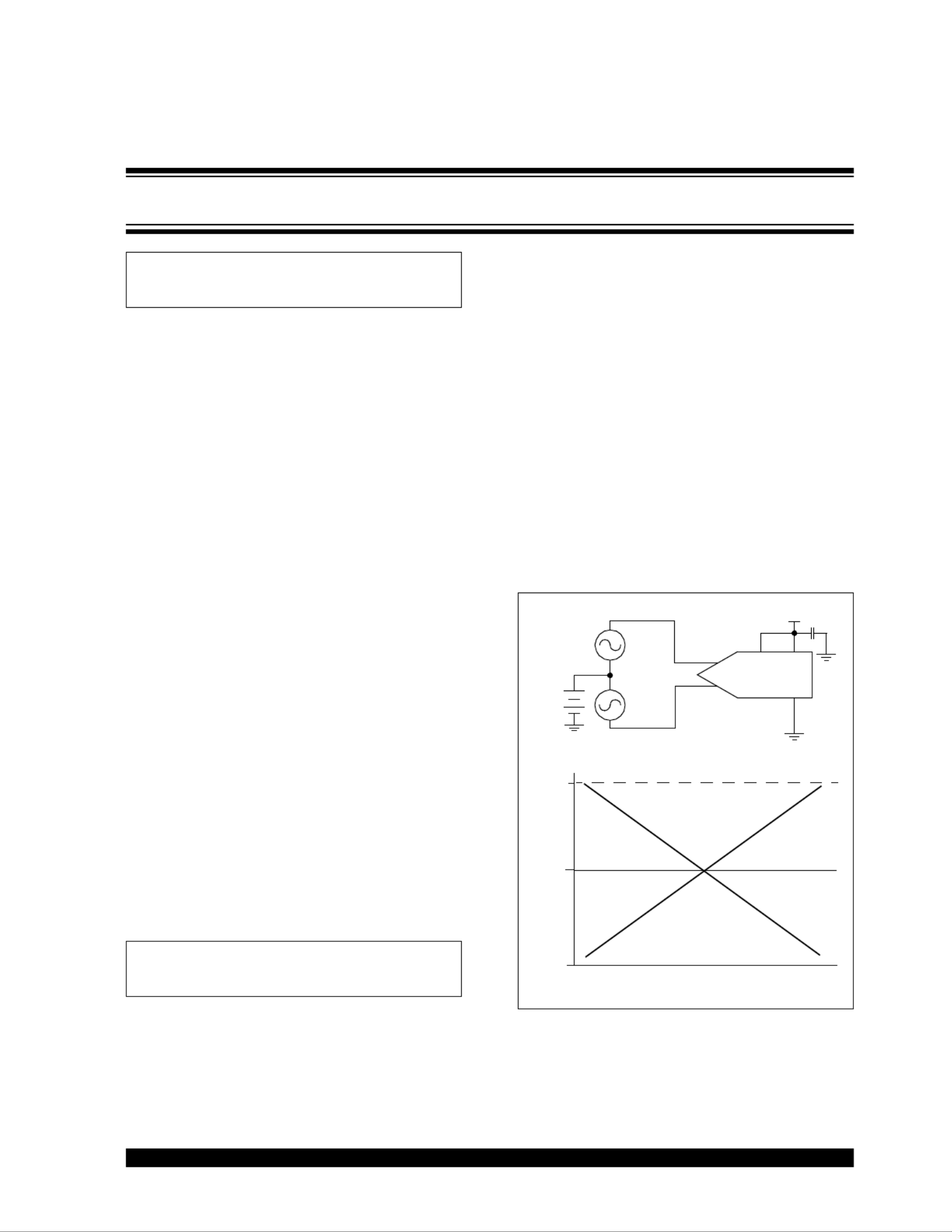
The circuit in Figure 1 shows a differential signal being
applied to the IN+ and IN- pins of the converter. This
method is referred to as full differential operation of the
converter. The graph below the circuit shows possible
voltage levels for a differential application. The inputs
are centered around a common mode voltage, VCM.
VREFis equal to the maximum input swing, shown here
as VDD. By setting V
REF equal to the maximum input
swing of the signal, the full range of the A/D converter
is being used.
FIGURE 1:Driving a true differential
converter with a true differential input.
Author:Craig L. King
Microchip Technology Inc.
Digital Code2n( )IN+IN-
–( )
2V REF
--------------------------------------=
VDD
1 µF
Input Signal
Differential VREF
p-p
VREF
p-p
VCM
-4096 +4095
Output Code
IN+
IN-
VREF
VDD
1/2VDD
GND
Voltage Levels (V)
VCM
IN+
IN-
VREF VDD
VSS
Differential ADC Biasing Techniques, Tips and Tricks
Product specificaties
| Merk: | Microchip |
| Categorie: | Niet gecategoriseerd |
| Model: | MCP3301 |
Heb je hulp nodig?
Als je hulp nodig hebt met Microchip MCP3301 stel dan hieronder een vraag en andere gebruikers zullen je antwoorden
Handleiding Niet gecategoriseerd Microchip

13 Januari 2026

12 Januari 2026

12 Januari 2026

12 Januari 2026

12 Januari 2026

12 Januari 2026

6 December 2025

5 December 2025

30 November 2025

30 November 2025
Handleiding Niet gecategoriseerd
Nieuwste handleidingen voor Niet gecategoriseerd

24 Januari 2026

24 Januari 2026

24 Januari 2026

24 Januari 2026

24 Januari 2026

24 Januari 2026

24 Januari 2026

23 Januari 2026

23 Januari 2026

23 Januari 2026