Festo CTEU-VN Handleiding
Festo Niet gecategoriseerd CTEU-VN
Bekijk gratis de handleiding van Festo CTEU-VN (6 pagina’s), behorend tot de categorie Niet gecategoriseerd. Deze gids werd als nuttig beoordeeld door 14 mensen en kreeg gemiddeld 4.8 sterren uit 8 reviews. Heb je een vraag over Festo CTEU-VN of wil je andere gebruikers van dit product iets vragen? Stel een vraag
Pagina 1/6
Translation of the original instructions
IO-Link
®
, LASAL
®
, SIGMATEK
®
, VARAN-BUS
®
are registered trademarks of the
respective trademark owners in certain countries.
1Intended use
The bus node type CTEU-VN has been designed exclusively for use as a parti-
cipant
in VARAN-BUS networks. The bus node may only be used in its original status
without unauthorised modifications and only in perfect technical condition.
The maximum limits must not be exceeded.
The product is suitable for industrial purposes only (ClassA). Measures for inter-
ference suppression may be required in residential areas (ClassB).
Detailed information on commissioning is provided in the documentation for the
higher-order control system.
Information on VARAN-BUS:
èwww.varan-bus.net
All available documents for the product www.festo.com/pk.è
1.1Training of qualified personnel
The product may only be commissioned by trained, qualified control and automa-
tion technology personnel, who are familiar with:
–mounting, installation, operation and diagnostics of control systems, net-
works and fieldbus systems
–applicable regulations for accident prevention and occupational safety
–the documentation for the product.
1.2Service
Consult your local Festo repair service if you have any technical problems.
2Safety
–Prior to assembly or installation work: switch off power supply and secure it
against being switched back on.
–For the electrical power supply, use only SELV circuits in accordance with IEC
60204-1/EN 60204-1.
–Observe the handling specifications for electrostatically sensitive devices.
–Seal unused connections with cover caps to achieve the required degree of
protection.
–Use connection hardware with the required degree of protection.
–Commission only a completely mounted and wired product.
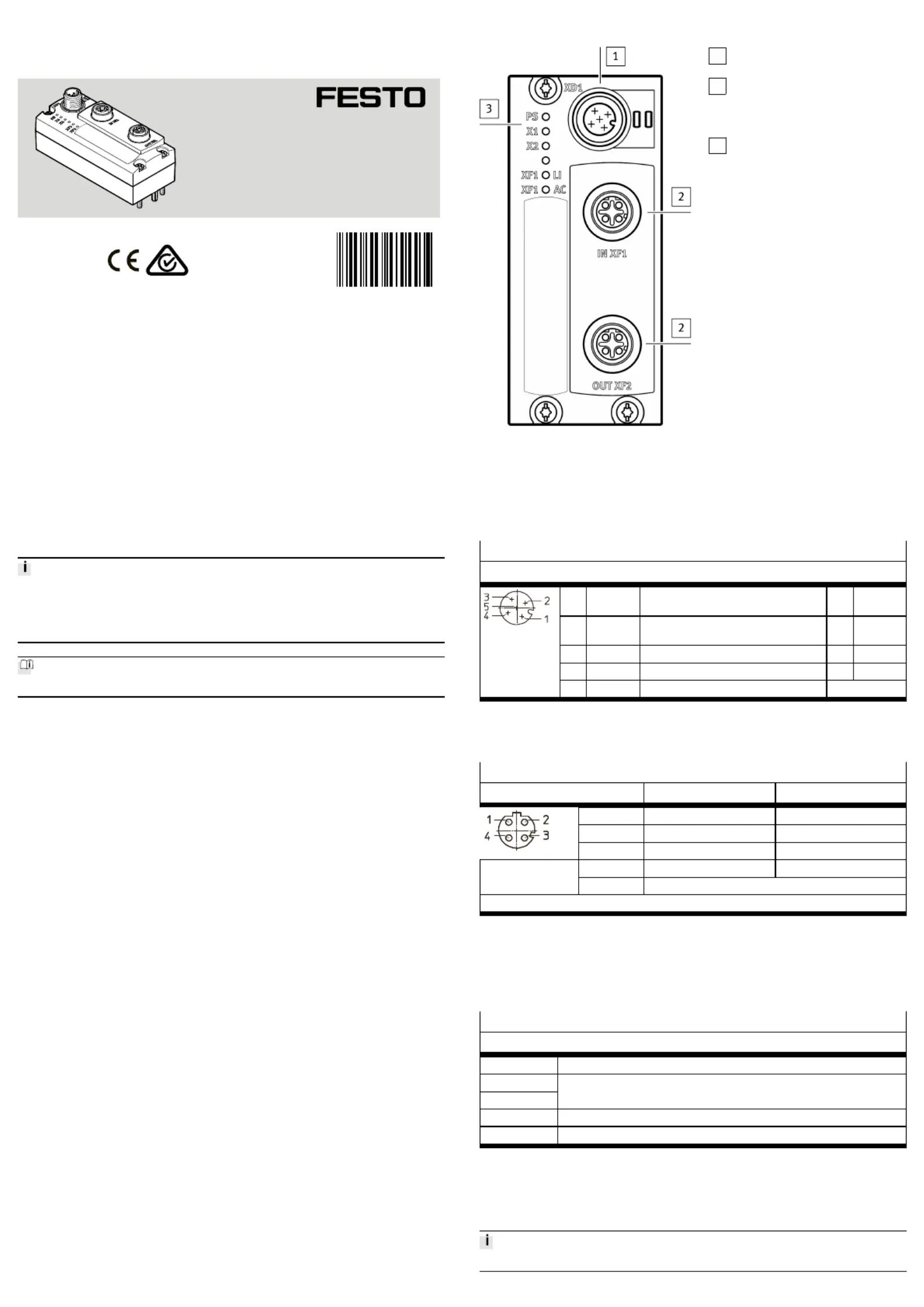
3Connections and displays
1
Power supply connection (XD1)
è3.2 Connections
2
Network connections (network
ports IN XF1,OUT XF2, fieldbus
interface)
è3.2 Connections
3
Status LEDs
è3.3 Displays,
è7 Diagnostics via LEDs
Fig. 1
3.1I-Port interfaces
The I-Port interfaces (X1/X2) are located on the underside of the bus node.
3.2Connections
Power supply connection XD1
1)
Pin allocation
124VOperating voltage for electronics/sensors
(power system)
PSU
EL/SEN
224VLoad voltage for valves/outputs (power
load)
PLU
VAL/OUT
30VOperating voltagePSU
EL/SEN
40VLoad voltagePLU
VAL/OUT
5FEFunctional earth
2)
FE
1) plug M12, 5-pin, A-coded
2) Secure connection to functional earth over the connected product Equipotential bondingè
Tab. 1
Network connections
1)
Pin allocationIN XF1
2)
OUT XF2
2)
1TX+RX+
2RX+TX+
3TX–RX–
4RX–TX–
Housing(Shield/functional earth)
3)
TX = transmitted data, RX = received data
1)
2 sockets M12, 4-pin, D-coded Observe installation guidelines and line specificationsè
2) Pin allocation with deactivated crossover detection
3) Secure connection to functional earth over the connected product Equipotential bondingè
Tab. 2
3.3Displays
Status LEDs
Meaning
PSStatus of operating and load voltage supplies
X1
X2
System status "I-Port Device 1" or "I-Port Device 2"
1)
XF1 LIConnection status IN XF1 ("Link")
2)
XF1 ACData reception IN XF1 ("Active")
1) Accessories with two I-port interfaces required to connect two products, e.g. the decentralised electric sub-
base CAPC.
2) VARAN-BUS-Status. When using the Festo Field Device Tools (FFT), e.g. for a firmware update: Ethernet
status.
Tab. 3
Additional information 7 Diagnostics via LEDs.è
8094069
CTEU-VN
Bus node
8094069
2018-10
[8094071]
Instructions| Operating| Bus node| VARAN-BUS
Festo SE & Co. KG
Ruiter Straße 82
73734 Esslingen
Germany
+49 711 347-0
www.festo.com
Product specificaties
| Merk: | Festo |
| Categorie: | Niet gecategoriseerd |
| Model: | CTEU-VN |
Heb je hulp nodig?
Als je hulp nodig hebt met Festo CTEU-VN stel dan hieronder een vraag en andere gebruikers zullen je antwoorden
Handleiding Niet gecategoriseerd Festo

2 Augustus 2025

2 Augustus 2025

1 Augustus 2025

1 Augustus 2025

1 Augustus 2025

1 Augustus 2025

1 Augustus 2025

1 Augustus 2025

1 Augustus 2025

1 Augustus 2025
Handleiding Niet gecategoriseerd
Nieuwste handleidingen voor Niet gecategoriseerd

23 Januari 2026

23 Januari 2026

23 Januari 2026

23 Januari 2026

23 Januari 2026

23 Januari 2026

22 Januari 2026

22 Januari 2026

22 Januari 2026

22 Januari 2026